From ancient civilizations to modern societies, humans have revered plants for their medicinal, psychotropic, and spiritual benefits. Notably, botanicals like hops and cannabis have long been a part of this narrative of human civilization. Yet, it was only through recent scientific strides that many of these effects stemmed from an intricate class of compounds known as terpenes.
Terpenes, with their diverse aromatic profiles and therapeutic potential, represent an intersection between nature’s bounty and human ingenuity. These compounds and their effects, stand as testament to the incredible symbiosis between humanity and plants.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes represent a diverse group of organic compounds ubiquitous in nearly every plant species worldwide. Profoundly aromatic, these compounds are integral to the composition of essential oils. Commonly sourced from plants such as citrus fruits, conifers, mint, lavender, and camphor, terpenes have long been recognized for their aromatic properties.
As mentioned above, even though the medicinal use of plants dates back millennia, our scientific comprehension of why plants delivered these effects is a recent one. More recent still is our growing understanding of how frequently terpenes play a role in a plants therapeutic potential.
Just look at present-day herbal medicine, which frequently incorporates terpene-rich plants and even essential oils due to their anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), antimicrobial, and sedative properties.
These compounds are widely employed in aromatherapy and are subject to extensive research as potential alternatives to pharmaceuticals for addressing pain, anxiety, inflammation, microbial infections, and more.
As research evolves, terpenes are poised to assume an increasingly prominent role in medical applications. Whether utilized in isolation or in conjunction with other plant-derived compounds like cannabinoids, terpenes may steer healthcare towards a more holistic, plant-centric paradigm.
How Many Different Terpenes Are There?
Terpenes are incredibly prolific and varied across the plant kingdom, even showing up in some types of fungi. There are more than 55,000 known terpenes (1), with 200+ found in the cannabis plant alone. Clearly, there is a lot of potential combinations, aromas — and possible health benefits.
If we look at cannabis specifically, most strains contain dozens of different terpenes which make up a cultivar’s unique aromatic fingerprint. A few of the most common cannabis terpenes include myrcene, limonene, pinene, beta-caryophyllene, ocimene, and linalool, among others. In fact, many terpenes present themselves in such small amounts that without proper standards to calibrate equipment to highly sensitive limits, you’d never know they are there.
What Are Cannabis-Derived Terpenes?
Cannabis terpenes are terpenes derived from the cannabis plant (a.k.a hemp, marijuana, etc.) These terpenes contribute to how weed smells, as well as to the effects and experience of the person using it. From OG Kush to Chem Dawg to GMO (Garlic Cookies), the strains we all know and love are all unique thanks to their remarkably varied terpene profiles.
Beyond the obvious flavor and aromatic distinctions, just a slight difference in terpene profile can make a big difference in how the strain affects mood and, potentially, health.
What are the most common cannabis terpenes? There are about 20 specific terpenes that tend to give this plant its telltale aromatic profile. As an example, myrcene is the most common terpene (2) (yet, it’s not necessarily the dominant terpene in any given plant).
Common cannabis terpenes:
Myrcene
Limonene
Pinene
Beta-Caryophyllene
Ocimene
Terpinolene
Alpha-Humulene
Linalool
Eucalyptol
Alpha-Phellandrene
Alpha-Terpinene
Guaiol
3 Carene
Camphene
Fenchol
P-Cymene
Sabinene
Valencene
Nerolidol
Borneol
What Is a Weed Terpene Profile?
Like we explained above, every strain of weed has a unique terpene profile. A weed terpene profile is like a chemical fingerprint.
Yet interestingly, with so much of the industry made up of extracts these days, many of these aromatic properties are frequently missing from the final extraction. This is because when cannabis is extracted or distilled, the harsh processing conditions end up removing most of the terpenes. Whether it’s CO2, butane, or ethanol extraction, the end result is frequently just a high cannabinoid, low terpene concentrate.
Which is why many manufacturers add pure terpenes back to the cannabis product in a post-extraction process. Here, manufacturers have a lot of room to play with, whether it’s matching the original strain scent or boosting it with other botanically derived flavors.
At Lab Effects, we offer both. We also help customers create customized weed terpene profiles based on their own existing cannabis flower and extracts, using cannabis profile matching.
Disclaimer: Terpenes are non-polar, oil-based hydrocarbons that, in pure form, can be very potent and sometimes volatile, flammable, and even corrosive compounds. For this reason, they should strictly be used by experienced and trained manufacturers, and we advise those who are unfamiliar with these compounds to exercise caution.
Popular Weed Terpenes and Effects
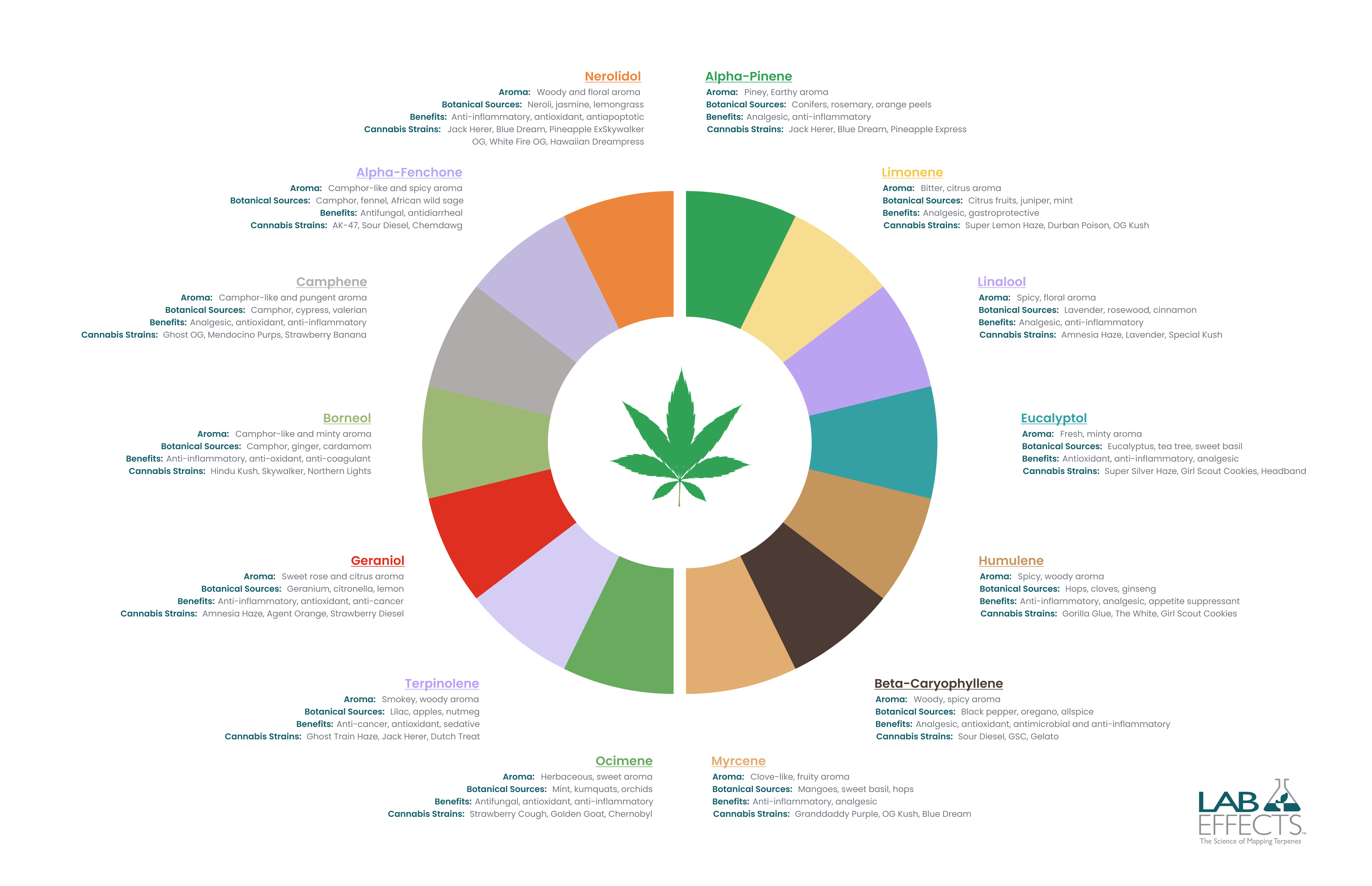
Over the last several decades, researchers have discovered many terpenes have interesting therapeutic effects. Below are some of the most notable science-backed claims about terpenes, as well as a bit of information about the botanical and cannabis strain sources where these compounds are commonly found.
- Alpha-Pinene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Conifer trees, rosemary, orange peels
- Therapeutic benefits: Analgesic (3), anti-inflammatory (4)
- Weed strains: Jack Herer, Blue Dream, Pineapple Express
-
- Limonene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Citrus fruits, juniper, mint
- Therapeutic benefits: Analgesic, gastroprotective (5)
- Weed strains: Super Lemon Haze, Durban Poison, OG Kush
-
- Linalool
-
-
- Botanical sources: Lavender, rosewood, cinnamon
- Therapeutic benefits: Analgesic (6), anti-inflammatory (7)
- Weed strains: Amnesia Haze, Lavender, Special Kush
-
- Eucalyptol
-
-
- Botanical sources: Eucalyptus, tea tree, sweet basil
- Therapeutic benefits: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic (8)
- Weed strains: Super Silver Haze, Girl Scout Cookies, Headband
-
- Humulene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Hops, cloves, ginseng
- Therapeutic benefits: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic (9)
- Weed strains: Gorilla Glue, The White, Girl Scout Cookies
-
- Beta-Caryophyllene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Black pepper, oregano, allspice
- Therapeutic benefits: Analgesic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory (10)
- Weed strains: Sour Diesel, GSC, Gelato
-
- Myrcene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Mangoes, sweet basil, hops
- Therapeutic benefits: Anti-inflammatory (11), analgesic (12)
- Weed strains: Granddaddy Purple, OG Kush, Blue Dream
-
- Ocimene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Mint, kumquats, orchids
- Therapeutic benefits: Antifungal, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory (13)
- Weed strains: Strawberry Cough, Golden Goat, Chernobyl
-
- Terpinolene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Lilac, apples, nutmeg
- Therapeutic benefits: Anti-cancer, antioxidant (14), sedative (15)
- Weed strains: Ghost Train Haze, Jack Herer, Dutch Treat
-
- Geraniol
-
-
- Botanical sources: Geranium, citronella, lemon
- Therapeutic benefits: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer (16)
- Weed strains: Amnesia Haze, Agent Orange, Strawberry Diesel
-
- Borneol
-
-
- Botanical sources: Camphor, ginger, cardamom
- Therapeutic benefits: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-coagulant (17)
- Weed strains: Hindu Kush, Skywalker, Northern Lights
-
- Camphene
-
-
- Botanical sources: Camphor, cypress, valerian
- Therapeutic benefits: Analgesic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory (18)
- Weed strains: Ghost OG, Mendocino Purps, Strawberry Banana
-
- Alpha-Fenchone
-
-
- Botanical sources: Camphor, fennel, African wild sage
- Therapeutic benefits: Antifungal, antidiarrheal (19)
- Weed strains: AK-47, Sour Diesel, Chemdawg
-
- Nerolidol
-
- Botanical sources: Neroli, jasmine, lemongrass
- Therapeutic benefits: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic (20)
- Weed strains: Skywalker OG, White Fire OG, Hawaiian Dream
Weed Terpenes Chart
Here’s a quick reference chart covering a few of the most common weed terpenes including identifiable aroma, botanical source, cannabis source, and possible therapeutic benefits.
Terpenes and Smell
When we bring a crystal coated bud to our nose for a whiff, what makes up this incredible smell? Smells typically aren’t made up of just one isolated terpene, but of many. A rainbow of aromas blending together to create a unique smell that our brain learns to recognize.
Smell starts in our nose, which contains a few million sensory neurons. Each neuron carries one of more than four-hundred types of odorant receptors (21) that are hyper-sensitive to the scent of different compounds.
These neurons are capable of distinguishing between familiar aromas like grapefruits and oranges, or lemons and lemongrass. As our brain learns to tag these complex odor profiles made up of a dozen or more terpenes to each food, flower, or strain that comes into our lives.
In cannabis, even if we can tell strains apart, few can learn to detect the individual terpenes that make up the larger terpene profile based on their sense of smell alone. Instead, the industry relies on lab analysis to break down the terpene profile behind each strain’s smell.
Terpenes Smell Chart
Yes, isolated terpenes each have a distinctive smell, but our human noses are often more familiar with a complex aromatic profile than with each terpene. For example, we might not be able to identify myrcene and limonene on their own, but many cannabis-connoisseurs would be able to ID a strain that contains a mixture of these as one with “diesel” genetics.
Still, it can be helpful to see the aromatic categories and their most commonly associated smells next to specific isolated terpenes. Here is an easy to use terpene smell chart for reference.
What Do Terpenes Taste Like?
Terpenes contribute to taste as well as smell. This is mainly because of the connection between smell and taste that creates the overall experience we call “flavor.” But, importantly, a terpene isn’t a flavor, it’s just a component of flavor.
In other words, flavors contain terpenes, but terpenes don’t contain flavors. But, let’s break this down starting with how we detect flavor.
The tongue and its taste buds only have the capacity to detect five “tastes” (22): sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. But, when our sense of smell becomes involved, we can experience a wider variety flavors, which is what our body detects when smell and taste are both in working order.
For example, we might say something tastes like strawberry, but if we have a cold and can’t smell it we might just taste a bit of sweet and a bit of sour. Add smell back in, and you get the full-bodied, red-berry, fruity flavor we associate with this fruit.
Here is another example. Limonene is a terpene commonly associated with lemons but it’s not the only contribution to the aromatic or flavor properties of this citrus. It’s one of more than a dozen different compounds that make up the complicity of smell and flavor for this tart citrus fruit. Yes, limonene may remind us of the aroma of lemons, but rest assured, in isolation it will definitely not taste like a lemon.
As a reminder: no one should ever be putting a pure terpene in their mouth. However, a skilled manufacturer can add terpenes to products and create unique smells and flavors. That’s where terpene effects truly shine when it comes to foods like edibles and beverages like craft beer.
FAQs
1. What are the most popular terpenes?
Some of the most common terpenes found in our favorite cannabis strains include:
- Alpha-Pinene
- Beta-Caryophyllene
- Humulene
- Linalool
- Limonene
- Ocimene
- Myrcene
- Terpinolene
2. What are the most common floral terpenes?
Some terpenes are best known for their floral scent. The most common are:
- Linalool
- Geraniol
- Nerolidol
3. What are the strongest terpenes?
Technically, terpenes aren’t “stronger” than each other. It’s our perception that varies, based on individual sensitivity and other circumstances.
A terpene that smells strongly to you might not smell the same to another person. You can even become less sensitive to certain smells, because once a certain threshold is reached, our olfactory senses simply shut that scent down.
Think of living in a house with a cat. You’ll become accustomed to the smells owning a cat involves, and won’t even notice them anymore after a certain level of scent is reached.
However, another person entering your home might be able to instantly smell that you have a cat. Similarly, the way terpenes contribute to scents isn’t based on how “strong” they are, but on how strongly your senses react to them.
Get Superior Effects With Lab Effects Terpenes
Getting the most out of terpenes is only possible if you have access to the best quality from the purest sources available. LabEffects’ terpenes are designed to make experiences better by adding aromatic enjoyment and familiarity to a wide range of products.
- Take advantage of both cannabis-derived strains and natural terpene flavors.
- Enjoy peace of mind knowing we use only 100% natural, plant-derived sources.
- Keep your products free from artificial additives or chemicals.
- Get a guarantee that your purchased terpenes are always pure and consistent.
- Leverage terpene blends customized to your precise preferences.
Order cannabis terpenes wholesale today from a reputable company in the U.S. cannabis industry. Lab Effects is cGMP-certified, ISO 9001-certified, HACCP-certified, FDA-registered, and ANAB-accredited.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8199371/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8326332/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26119957/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26119957/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30668410/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12587692/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11064-015-1629-7
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2013/502727/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/humulene
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8831077/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9319952/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9319952/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24012643/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24084350/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23339024/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7397177/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33892091/
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2013/459530/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7684460/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8235529/
- https://news.ucsb.edu/2023/020800/multifaceted-sensation
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6078535/#:~:text=Human%20taste%20can%20be%20distilled,salty%20and%20umami%20or%20savory